LINK
当ブログでも最近何度も登場しているGANですが、主に画像生成に使われるGANを、画像の顕著性マップの生成に使用している研究がありました。
顕著性マップ(Saliency Map)とは?
人が画像をみたときに注目しやすい場所を推定したヒートマップのことで、その歴史は非常に長く、簡単な所ではエッジなどのローレベルな特徴量を用いたり、様々な計算モデルが提案されています。
一方、GANは画像の生成部分と、生成された画像と訓練画像を見分ける認識器を同時に学習させる仕組みで、よりリアルな画像生成を行えるようになっています。
それらを組み合わせたのが今回提案されているSAN(Supervised Adversarial Networks)になります。
つまり、SANでは、顕著性マップを生成する部分と、生成されたマップと訓練データのマップを見分ける認識器を学習させています。

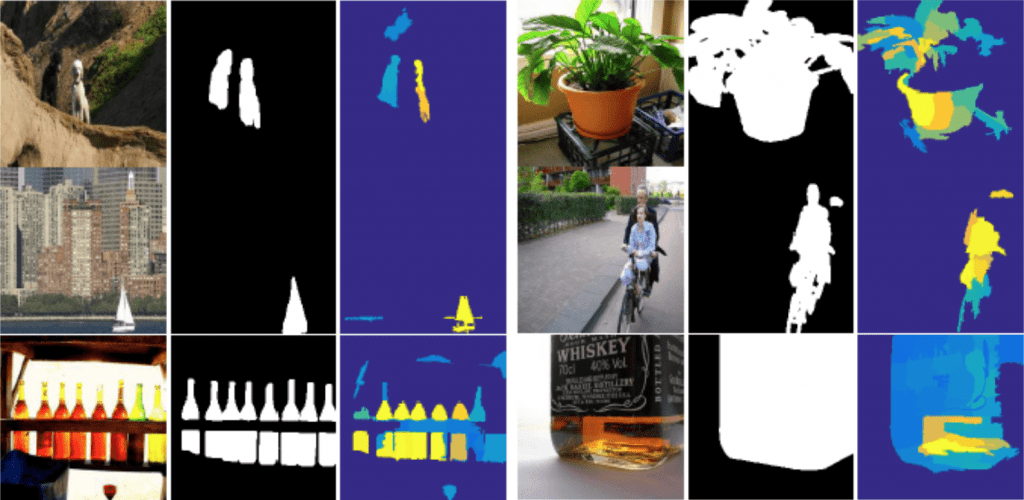
上の結果例では、一番左が入力画像、真ん中が正解の着目領域、一番右が推定された着目領域です。
一般的なGANの手法と異なるポイントとしては以下の2点です。
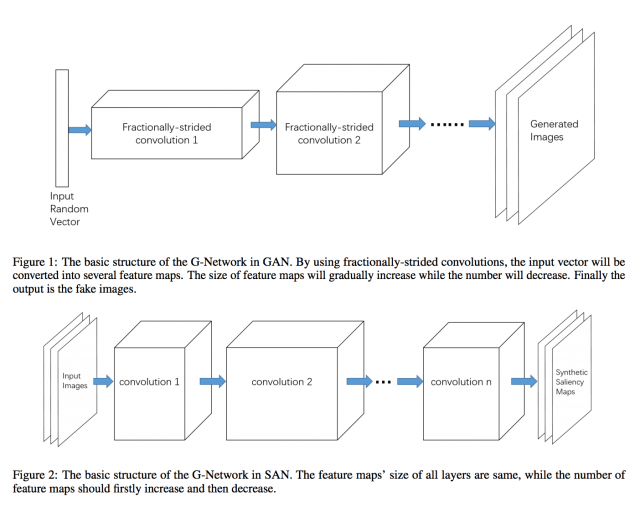
1.SaliencyMap生成までのネットワークで層のサイズを変えない。
GANでは下の図のFigure 1のように一度画サイズを減らしてマップ数を増やした上で最後に画サイズを大きくしていきますが、SANでは、画サイズを変えません。(Figure 2)これは、画像生成と違い、入力画像の位置構造が反映されたものが出力されるべきSaliencyMapの性質からすると、自然に思えます。
2.識別部分の学習において、クラス分類を導入する
生成データと訓練データの識別器の学習時、一般的なGANであれば嘘か本物かの2値分類になります。しかし、本研究によると、その場合簡単に識別器が両者を見抜いてしまい、勾配消失を起こしてしまうそうです。そのため、ここでは訓練データにあらかじめ付与されているクラス数Lを考慮したL+1 (1=生成データのクラス)クラスを識別するようにしています。より難しい識別をさせているということですね。
arXiv (24 Apr 2017 公開)
In the past few years, Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) became a prevalent research topic. By defining two convolutional neural networks (G-Network and D-Network) and introducing an adversarial procedure between them during the training process, GAN has ability to generate good quality images that look like natural images from a random vector. Besides image generation, GAN may have potential to deal with wide range of real world problems. In this paper, we follow the basic idea of GAN and propose a novel model for image saliency detection, which is called Supervised Adversarial Networks (SAN). Specifically, SAN also trains two models simultaneously: the G-Network takes natural images as inputs and generates corresponding saliency maps (synthetic saliency maps), and the D-Network is trained to determine whether one sample is a synthetic saliency map or ground-truth saliency map. However, different from GAN, the proposed method uses fully supervised learning to learn both G-Network and D-Network by applying class labels of the training set. Moreover, a novel kind of layer call conv-comparison layer is introduced into the D-Network to further improve the saliency performance by forcing the high-level feature of synthetic saliency maps and ground-truthes as similar as possible. Experimental results on Pascal VOC 2012 database show that the SAN model can generate high quality saliency maps for many complicate natural images.
